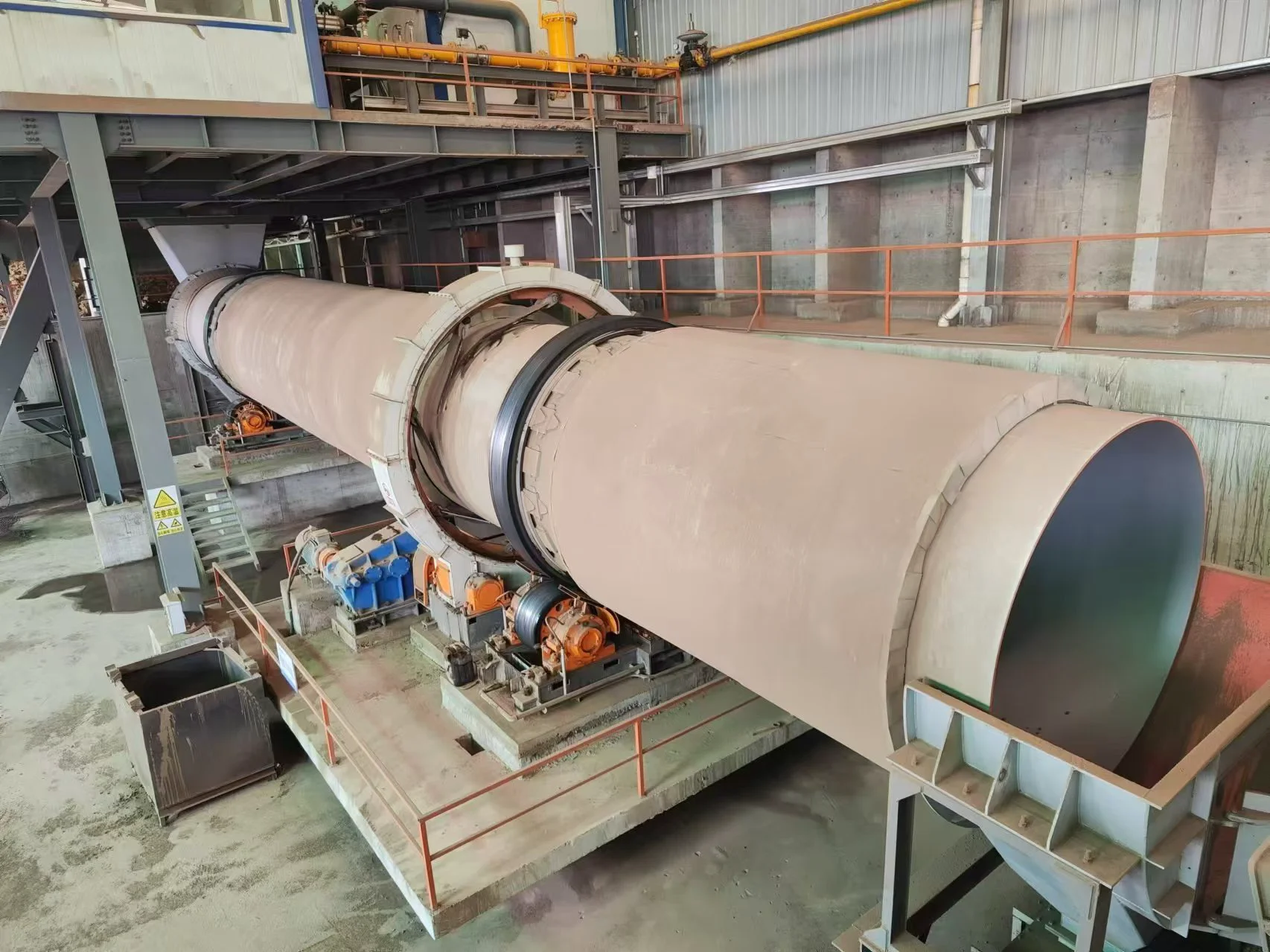
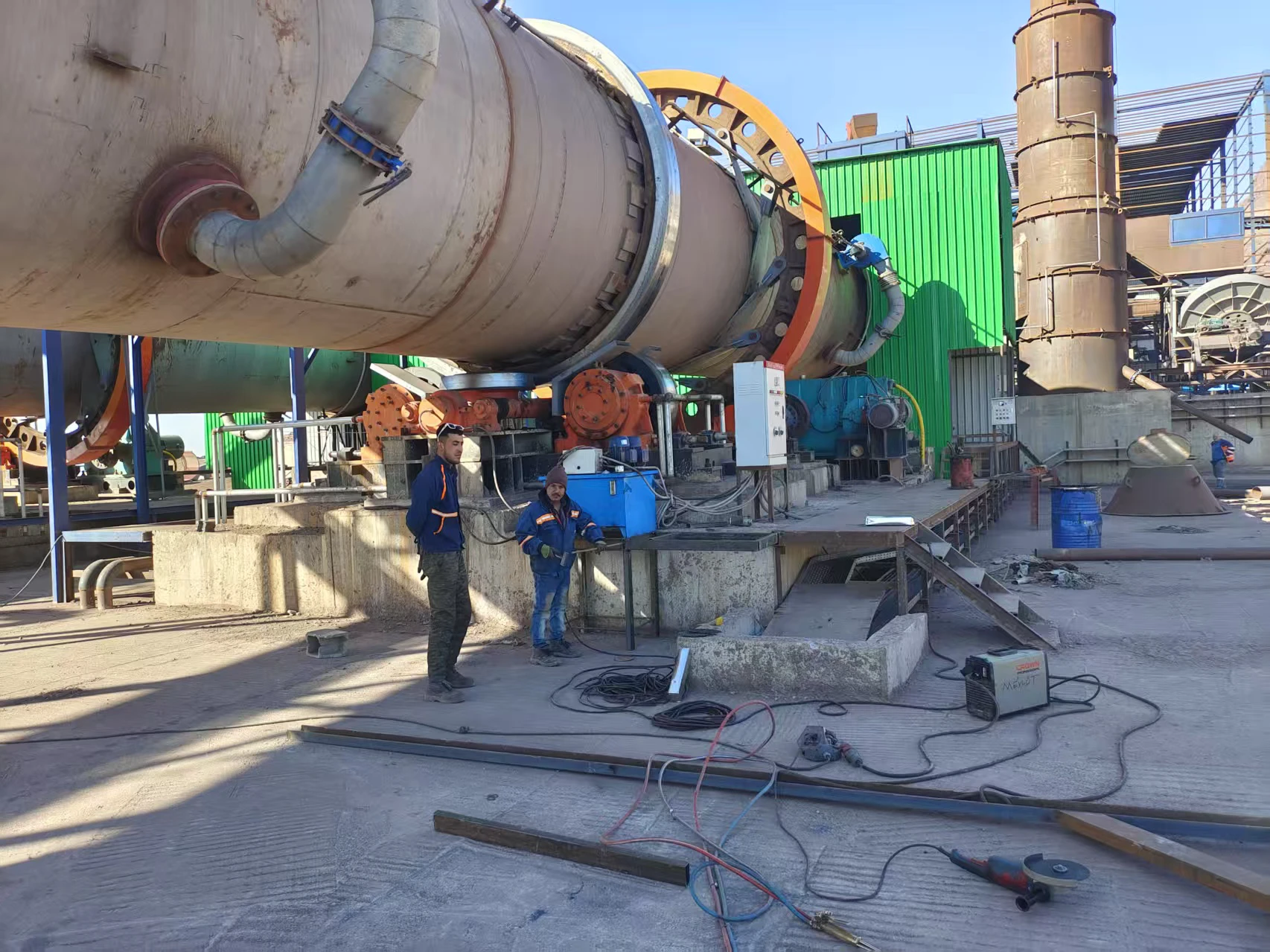
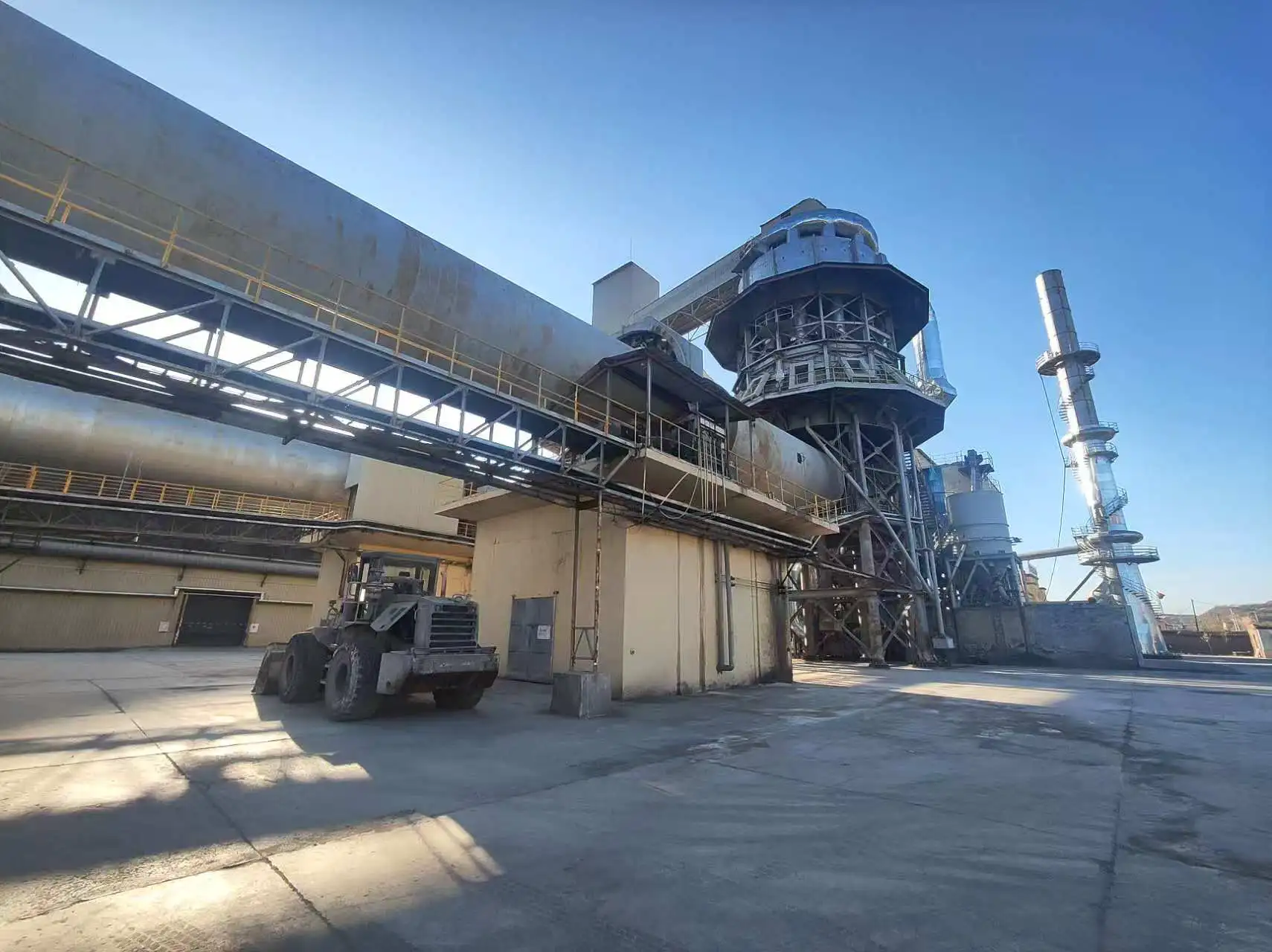
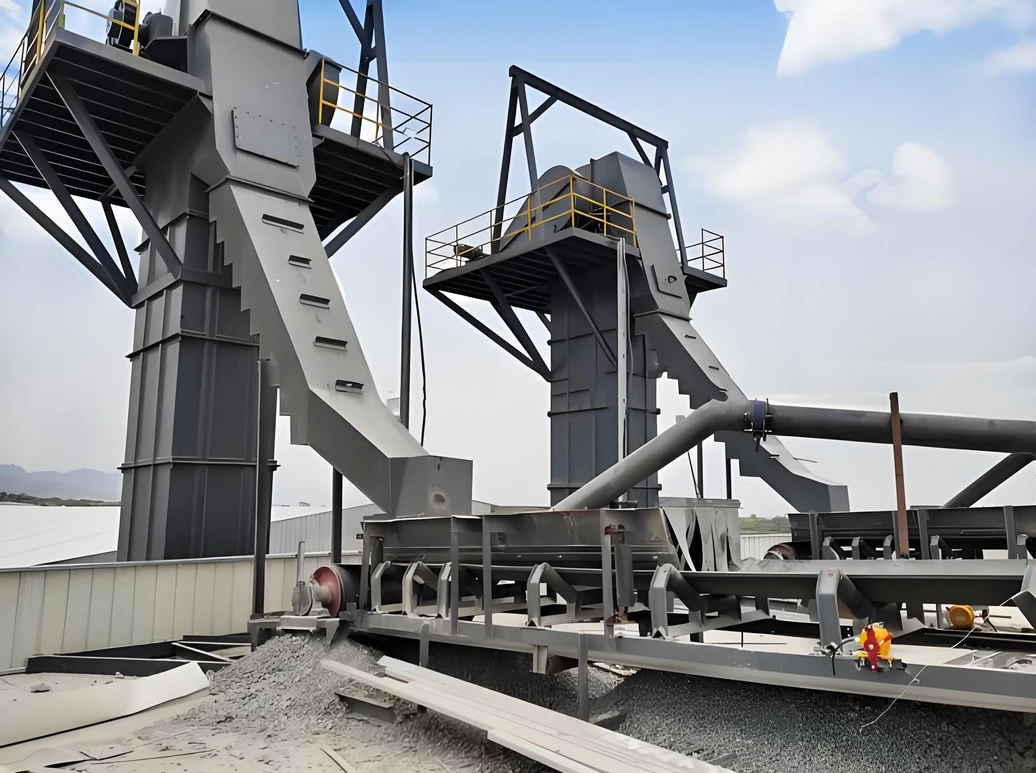
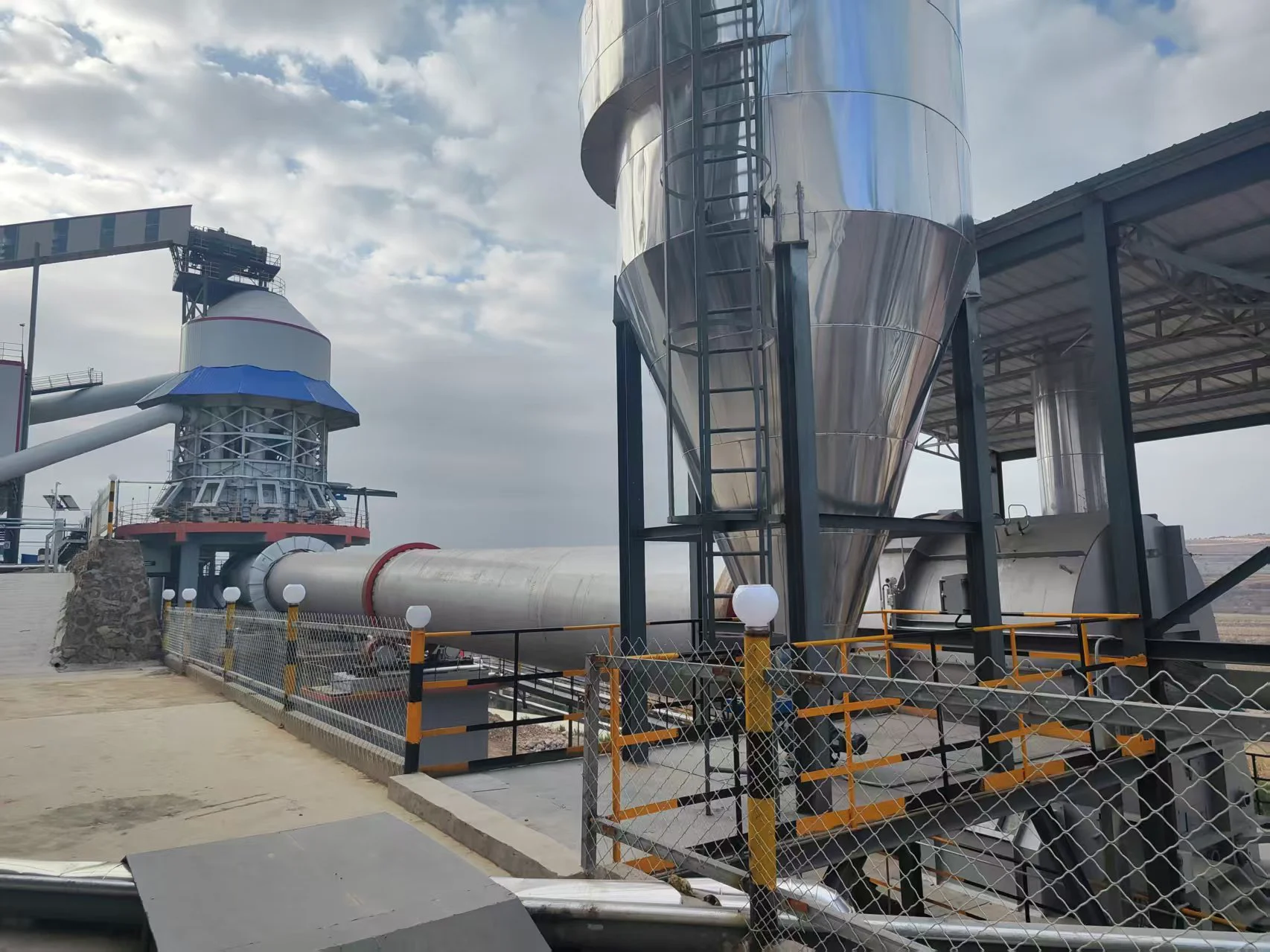
Calcined bauxite:
Bauxite, also known as alumina and bauxite, the main component is alumina,the density 2.4-2.5g/cm3 and hardness of 1 ~ 3, opaque, crisp, very difficult to melt, insoluble in water, can be dissolved in sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide solution.It is mainly for aluminum smelting and refractory materials.
Rotary kiln clinker is pale, pale yellow, and dark grey. It is mainly used for high aluminum refractory material, also can be used for production of fused corundum.
Light burning bauxite of rotary kiln,also known as the light burning powder,is the raw material of water purification agent aluminium polychloride.White or gray white,due to iron,it appears brownish yellow or light red.Density 3.9 ~ 4g/cm3, hardness 1 ~ 3, opaque, brittle.

The rotary kiln Calcined Bauxite changes can be divided into three sections: the decomposition stage, the two stage of mullite petrochemical and crystallization sintering stage.
1.Decomposition stage
400 ℃ -1200 ℃ temperature range is bauxite decomposition stage.Diaspore and kaolinite in bauxite at 400℃ start dehydration, 450-600 ℃ intense reaction, 700-800 ℃ completed.Gibbsite under high temperature gradually transformed corundum, kaolinite and dehydrated into metakaolin, more than 950 ℃ into mullite and amorphous SiO2,which is converted to cristobalite at high temperatures.
2.Mullite petrochemical phase
Above 1200 ℃, corundum and SiO2 continue to react to form mullite, is known as the secondary mullite:
3AI2O3 + 2SiO2 → (≥1200 ℃) → 3AI2O3 + 2SiO2 (secondary mullite)
In the secondary mullite petrochemical, it occurs about 10% volume expansion,while below the 1300-1400 ℃,Fe2O3, TiO2 of bauxite, and other impurities with Al2O3, SiO2 can form reaction liquid,liquid phase formation is contributed to secondary mullite formation,but also makes preparation for the sintering of barite.
3.Barite sintering stage
With the completion of secondary mullite petrochemical,Barite sintering rapid action is beginning.Above 1400-1500 ℃,due to the liquid phase, corundum and mullite crystals is growing,when 1500 ℃ is about 10μm, 1700 ℃ respectively 60μm and 90μm.
The main factors affecting the sintered bauxite are secondary mullite petrochemical phase,liquid and structure of bauxite.
Global mined bauxite,with more than 85% by using rotary kiln to produce alumina,followed by the production of aluminum metal.10% is used in the production of alumina using non-metallic, and the remaining for non-metallurgical bauxite applications.
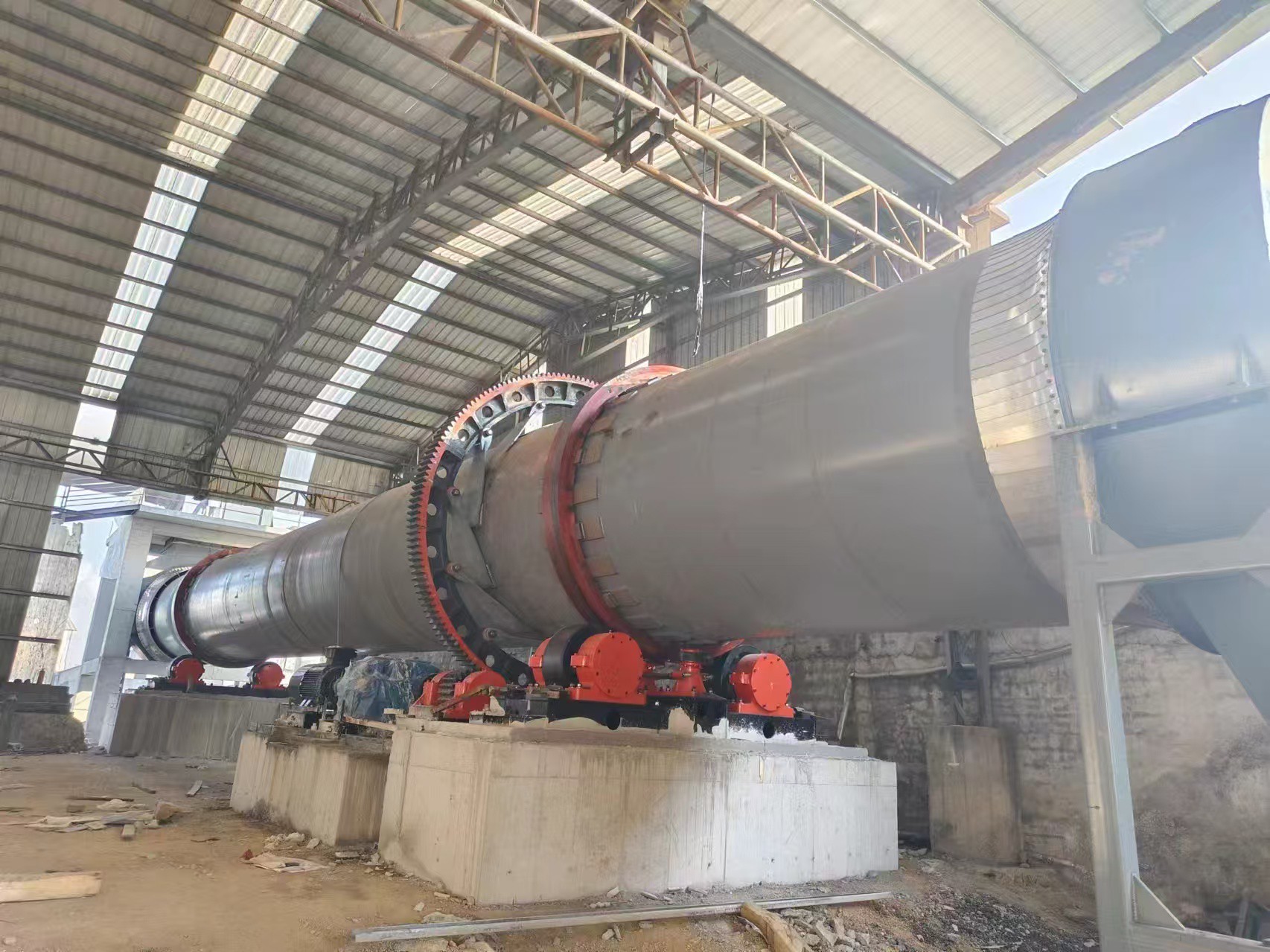

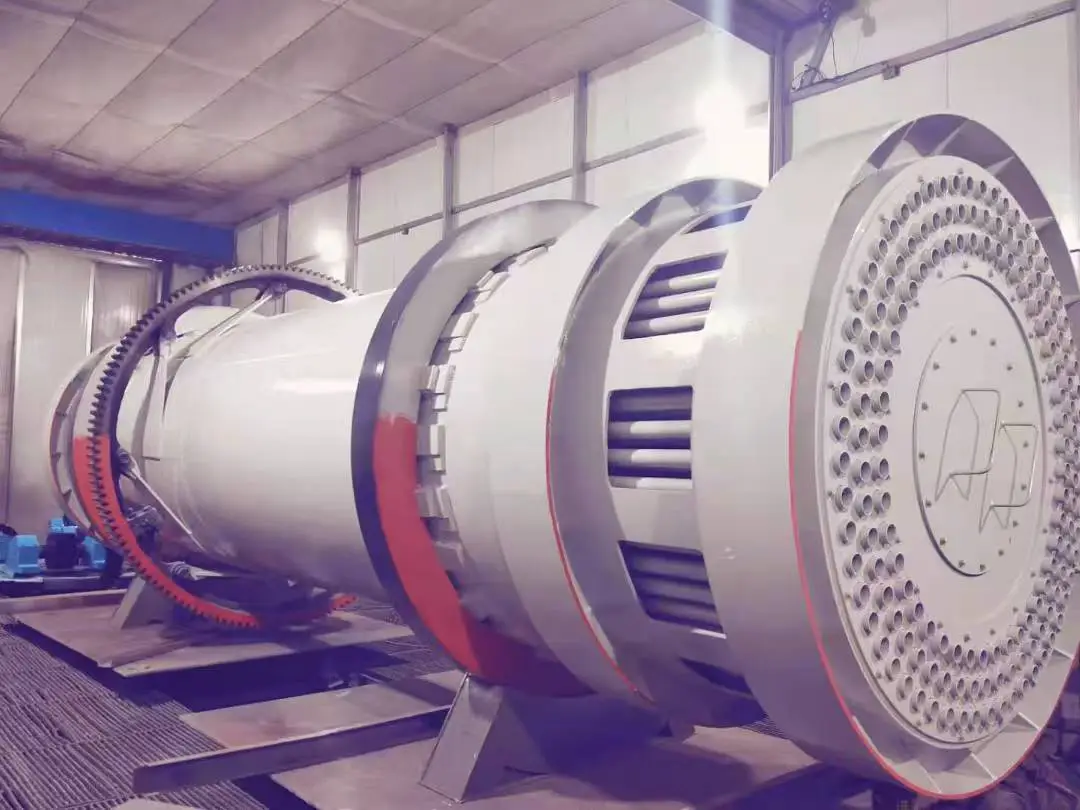
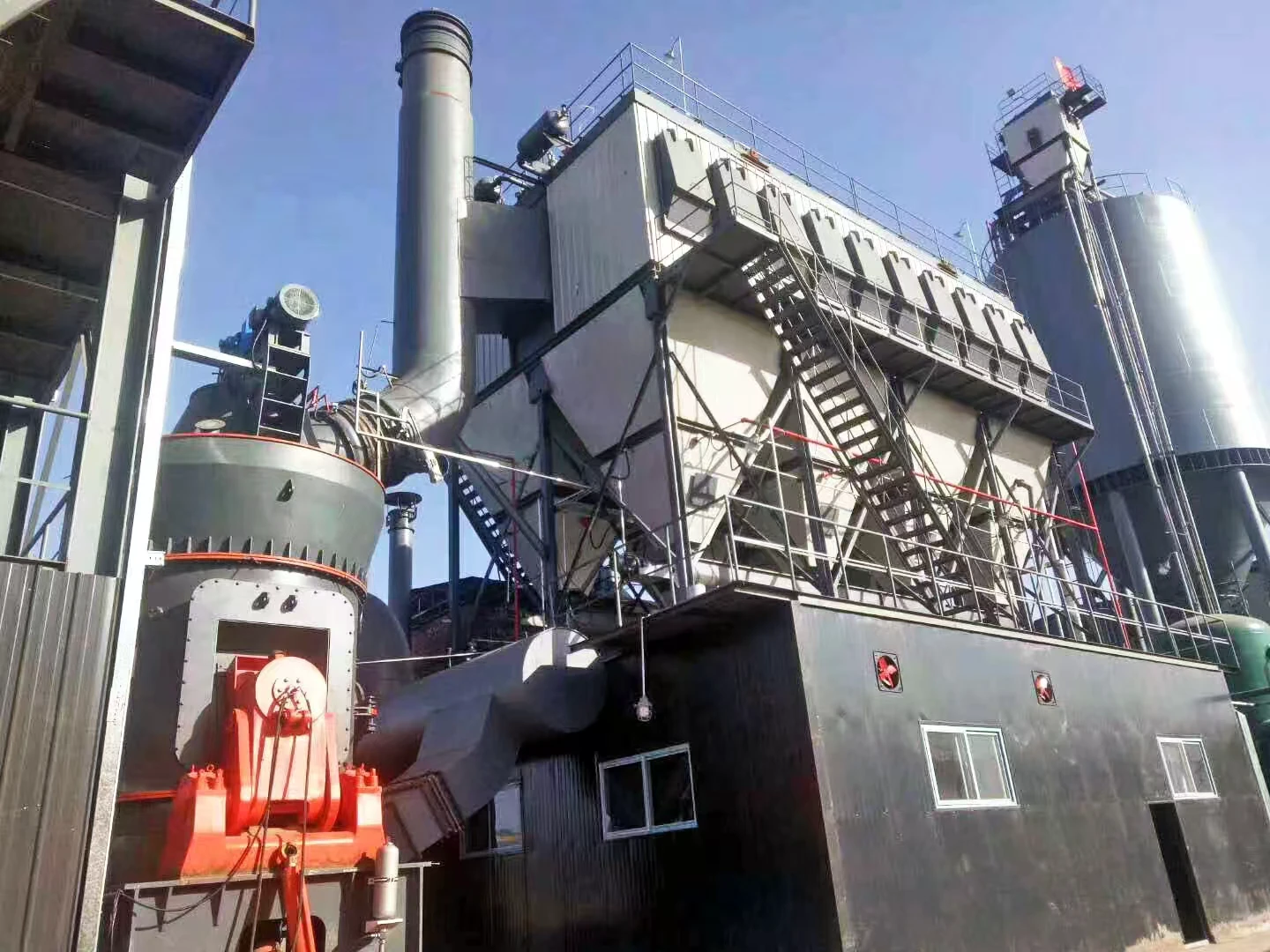
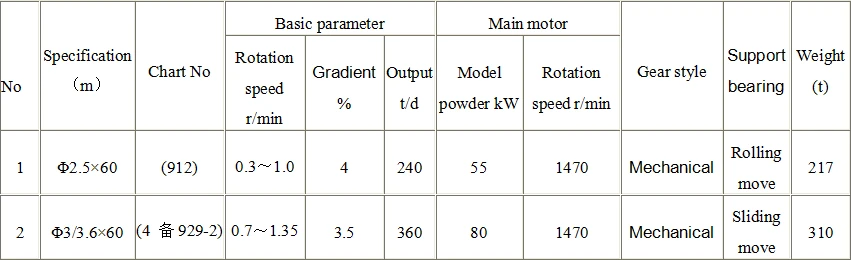
Rotary kiln parameters:
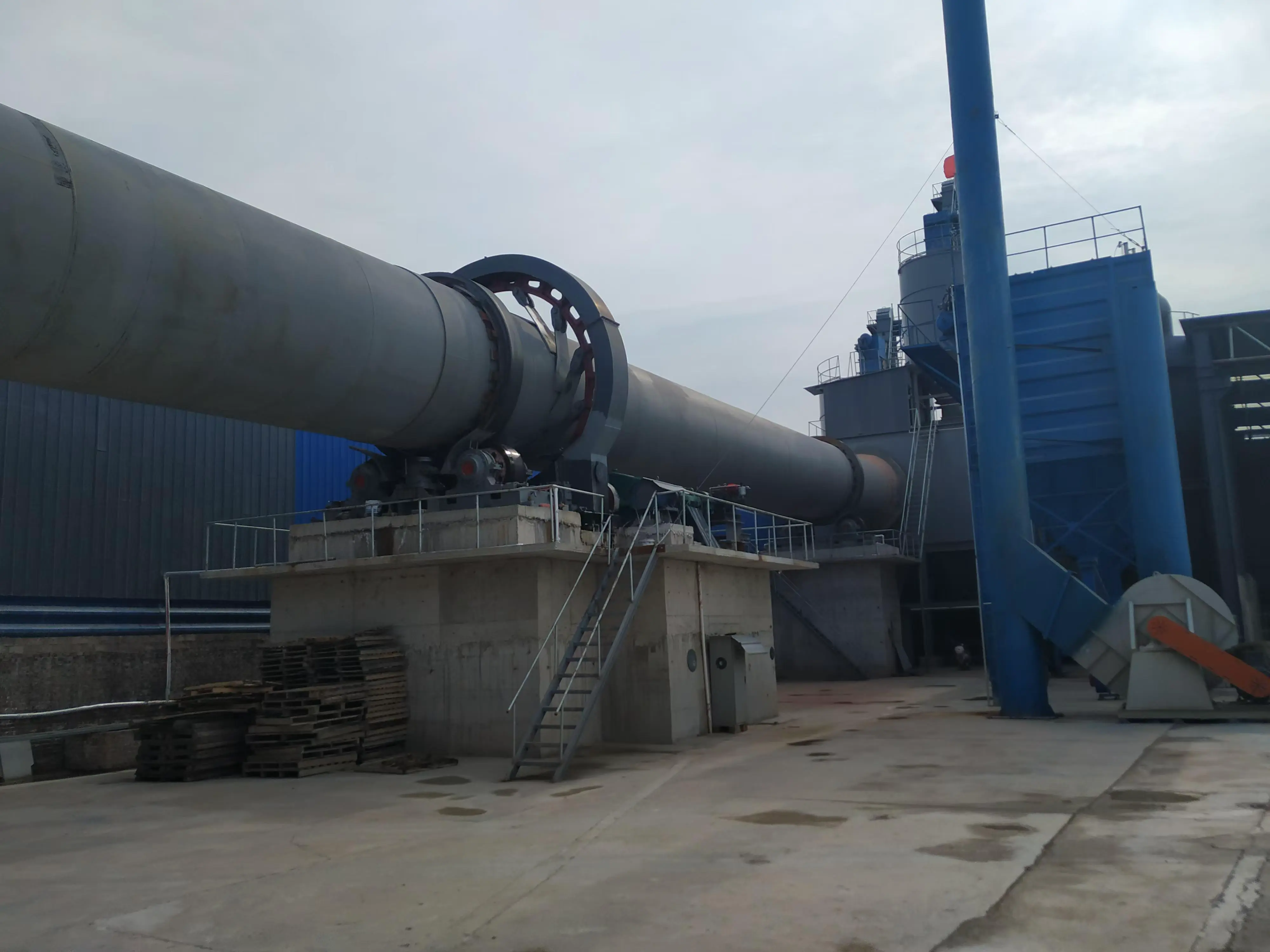
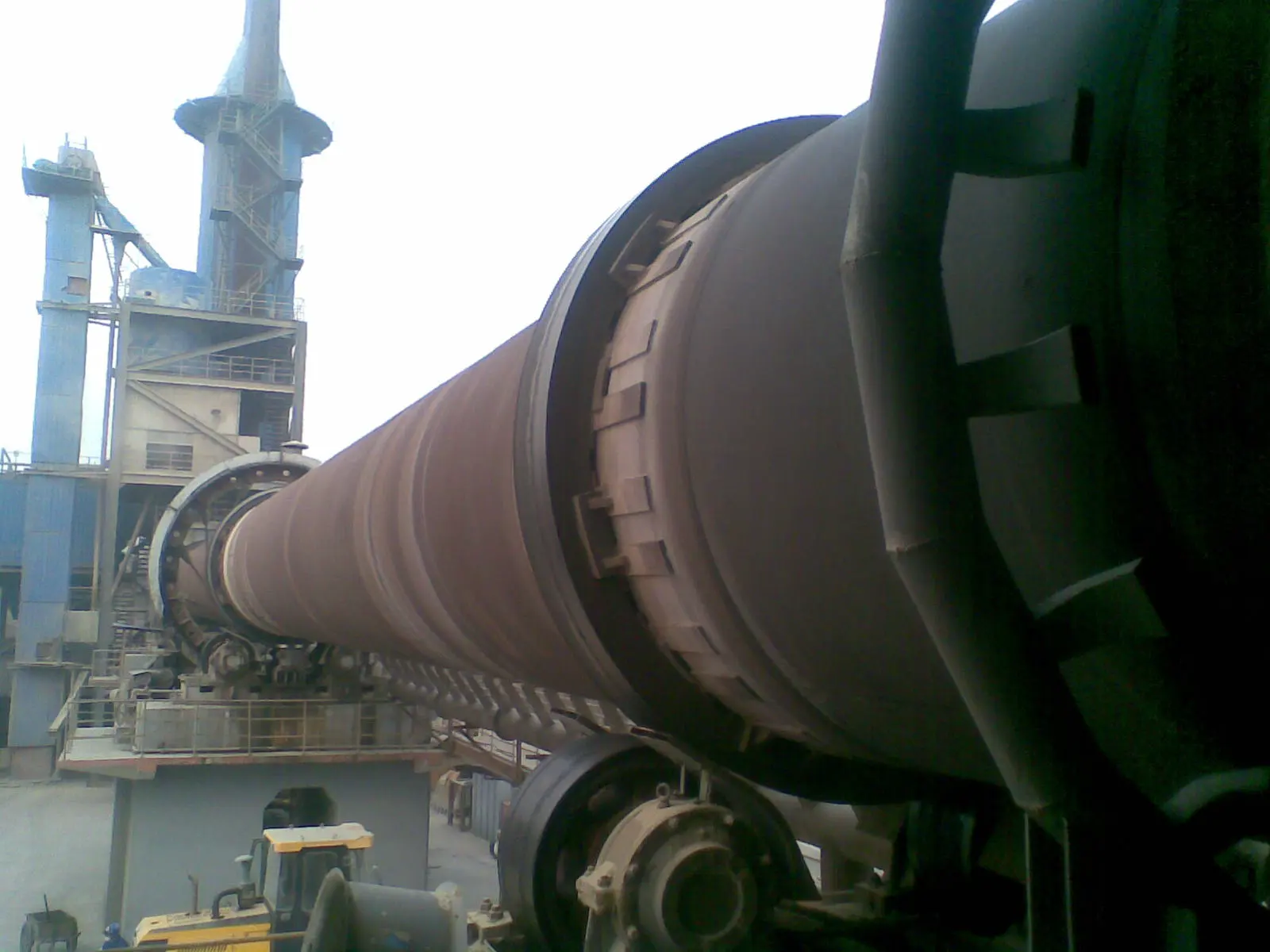
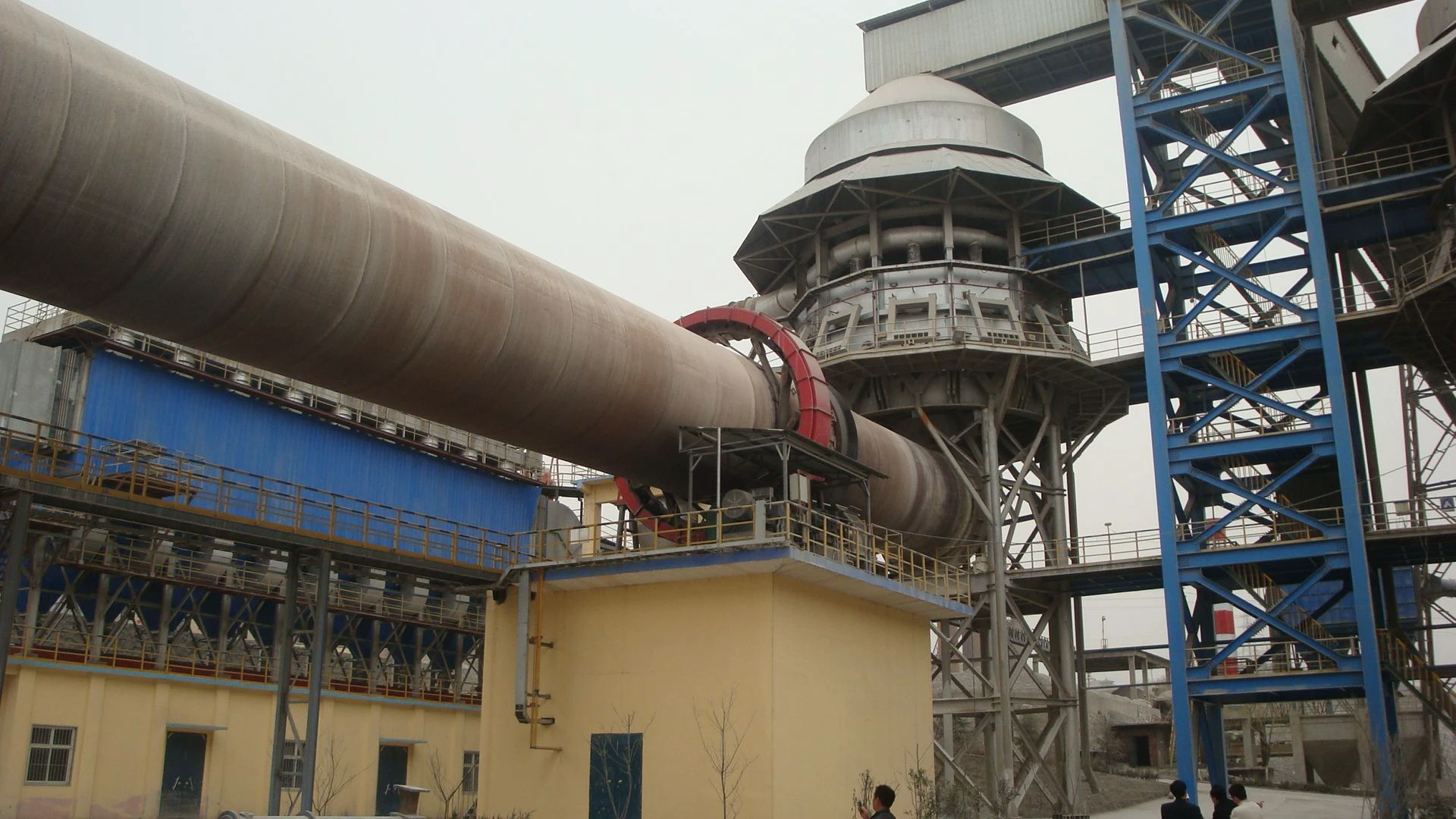
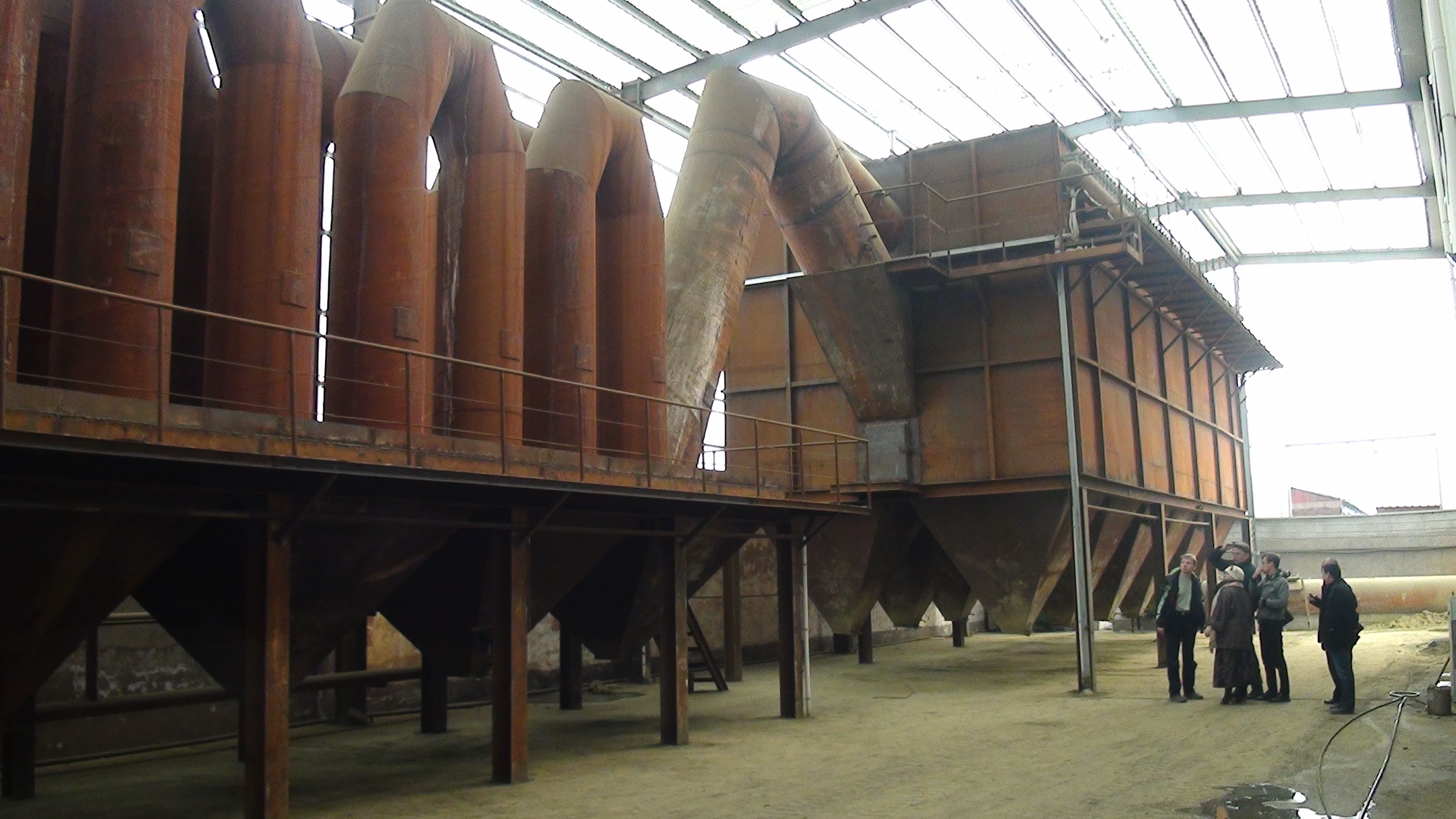
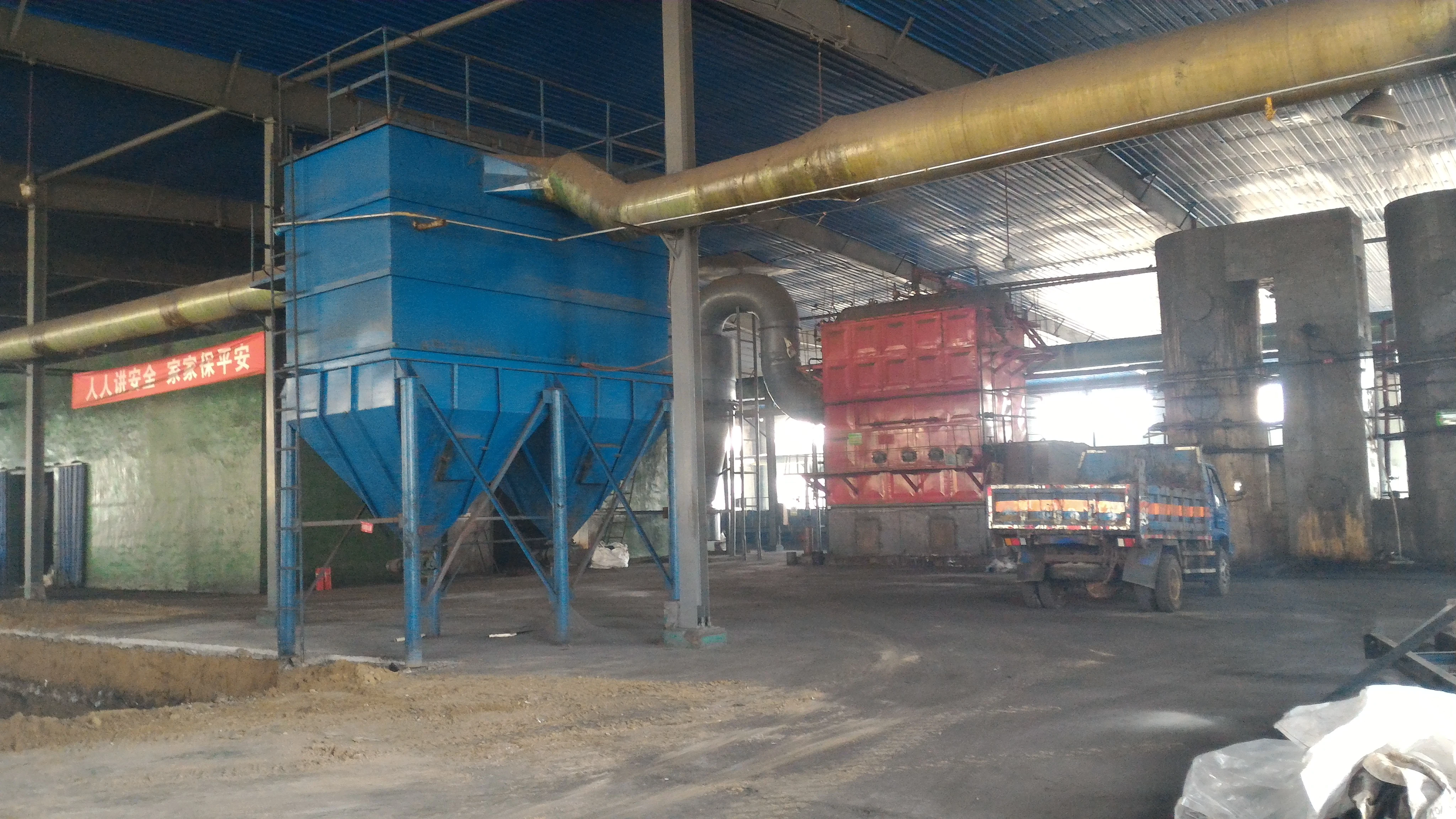
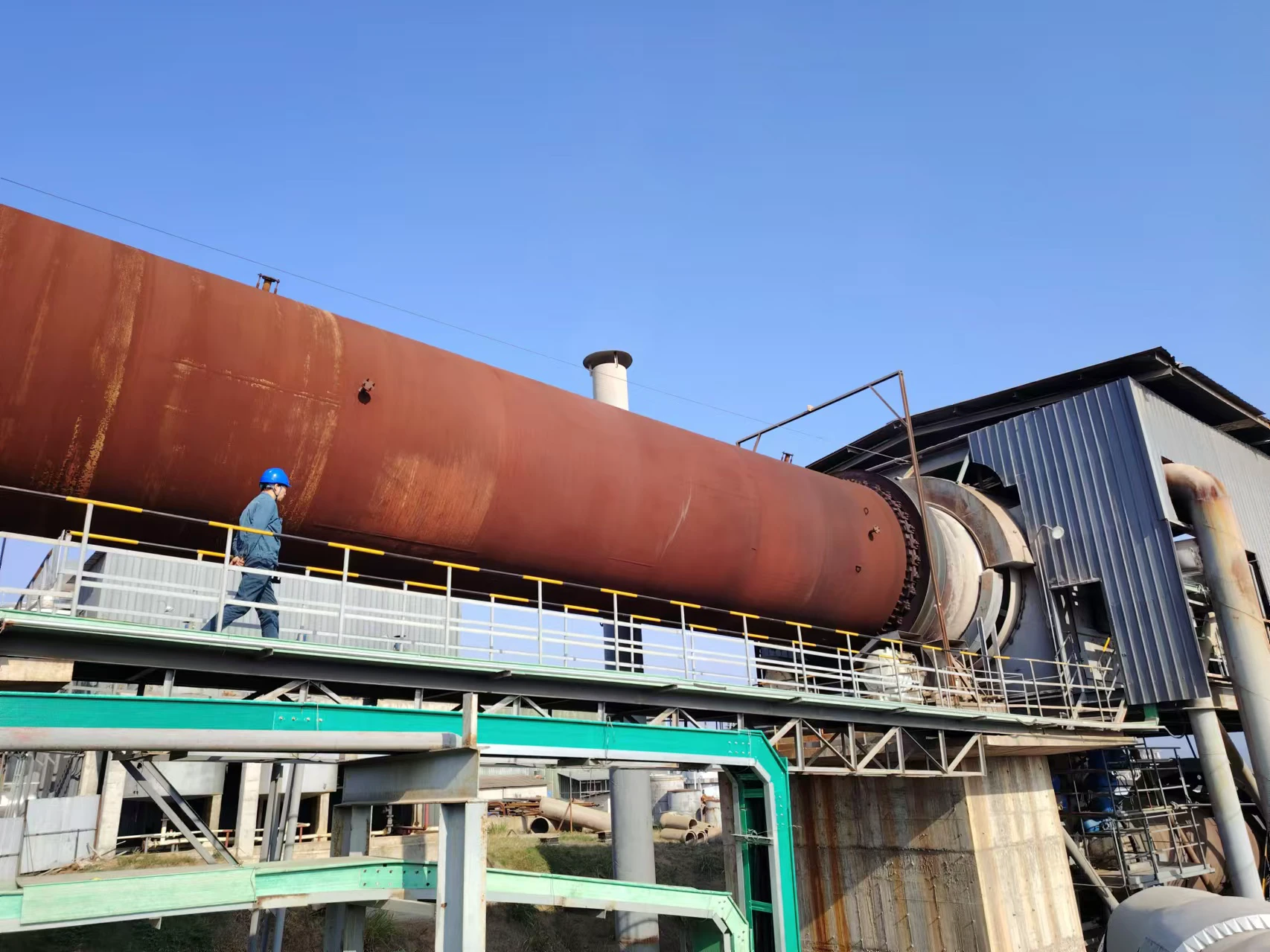
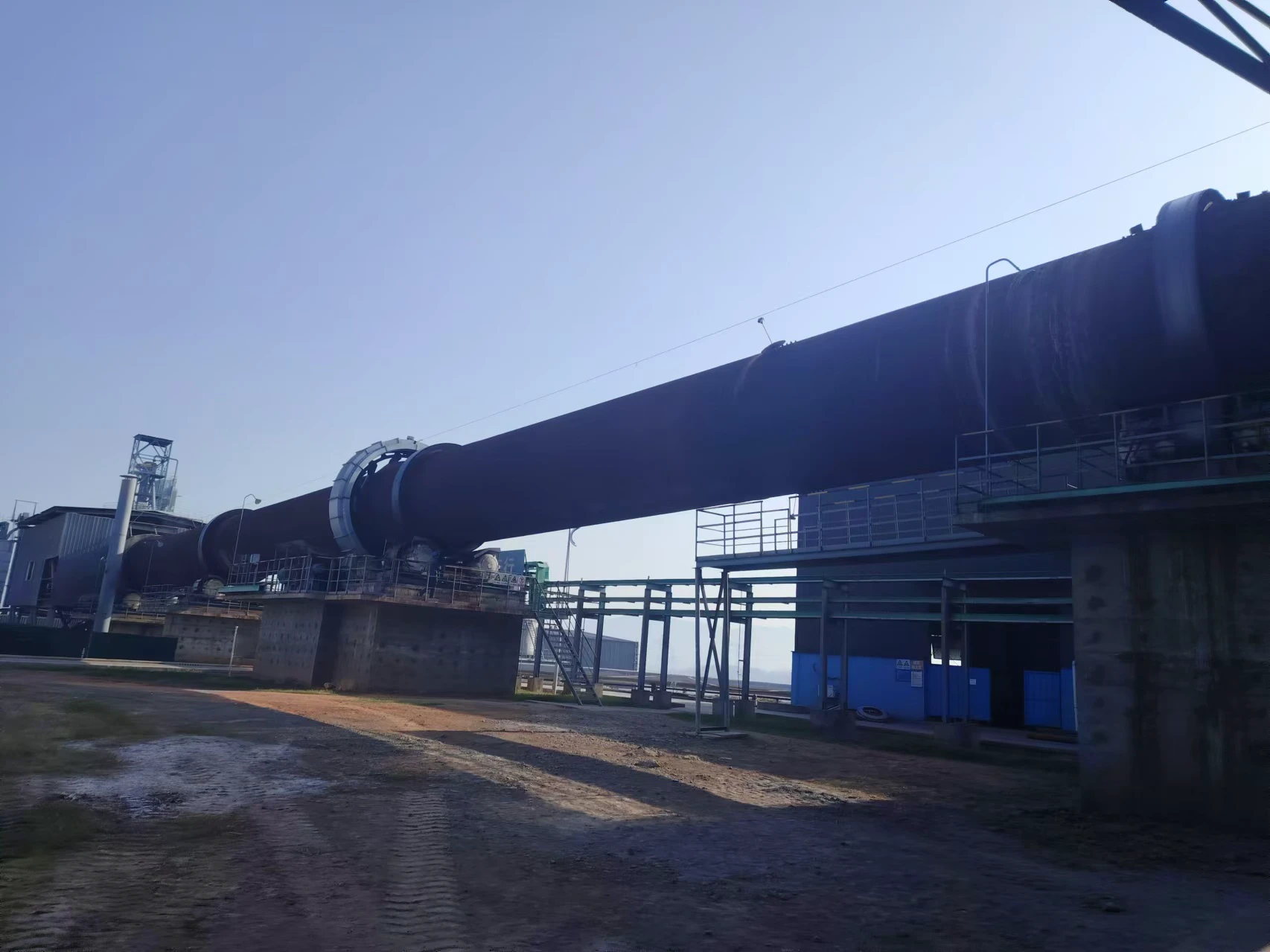
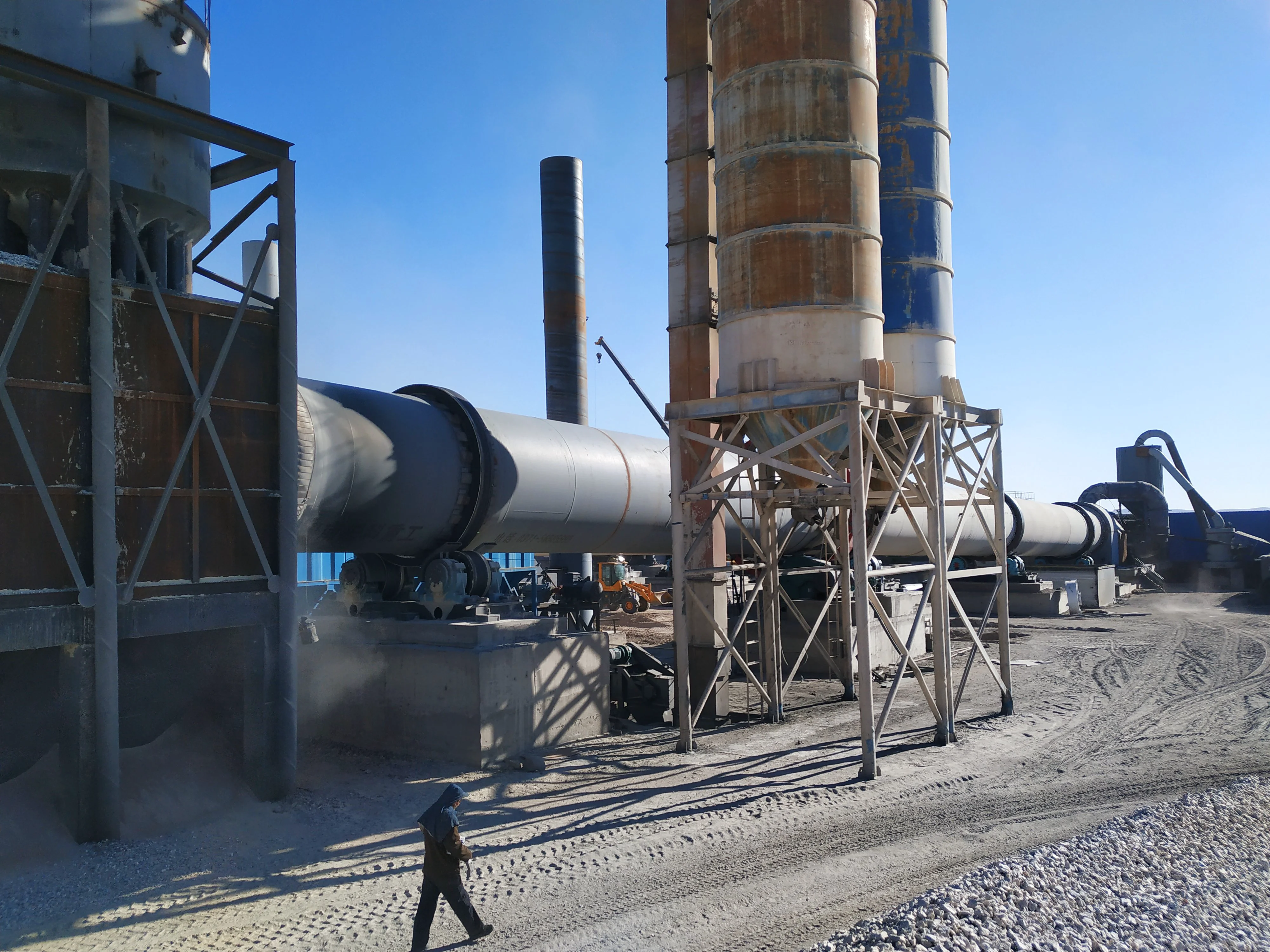
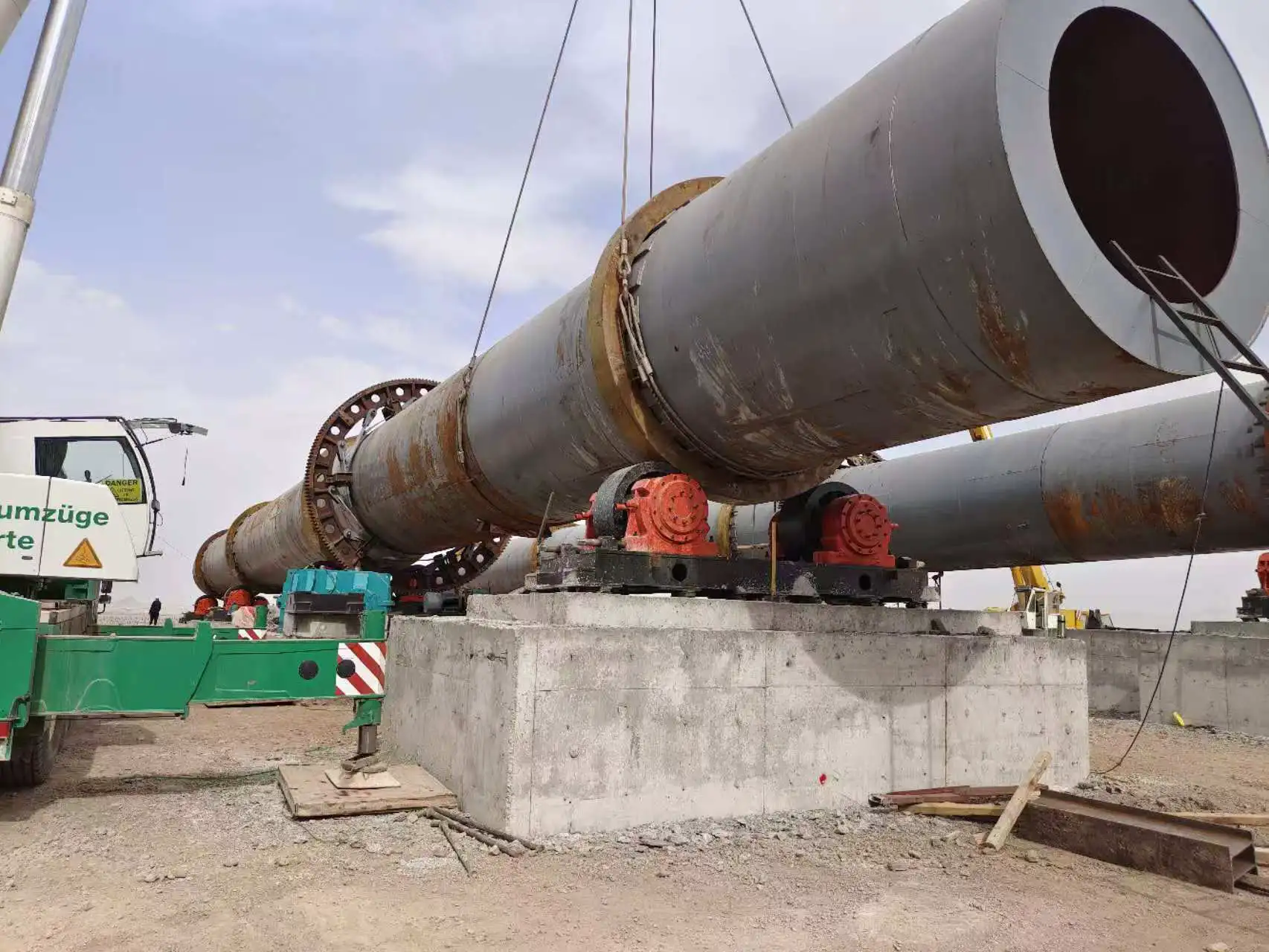
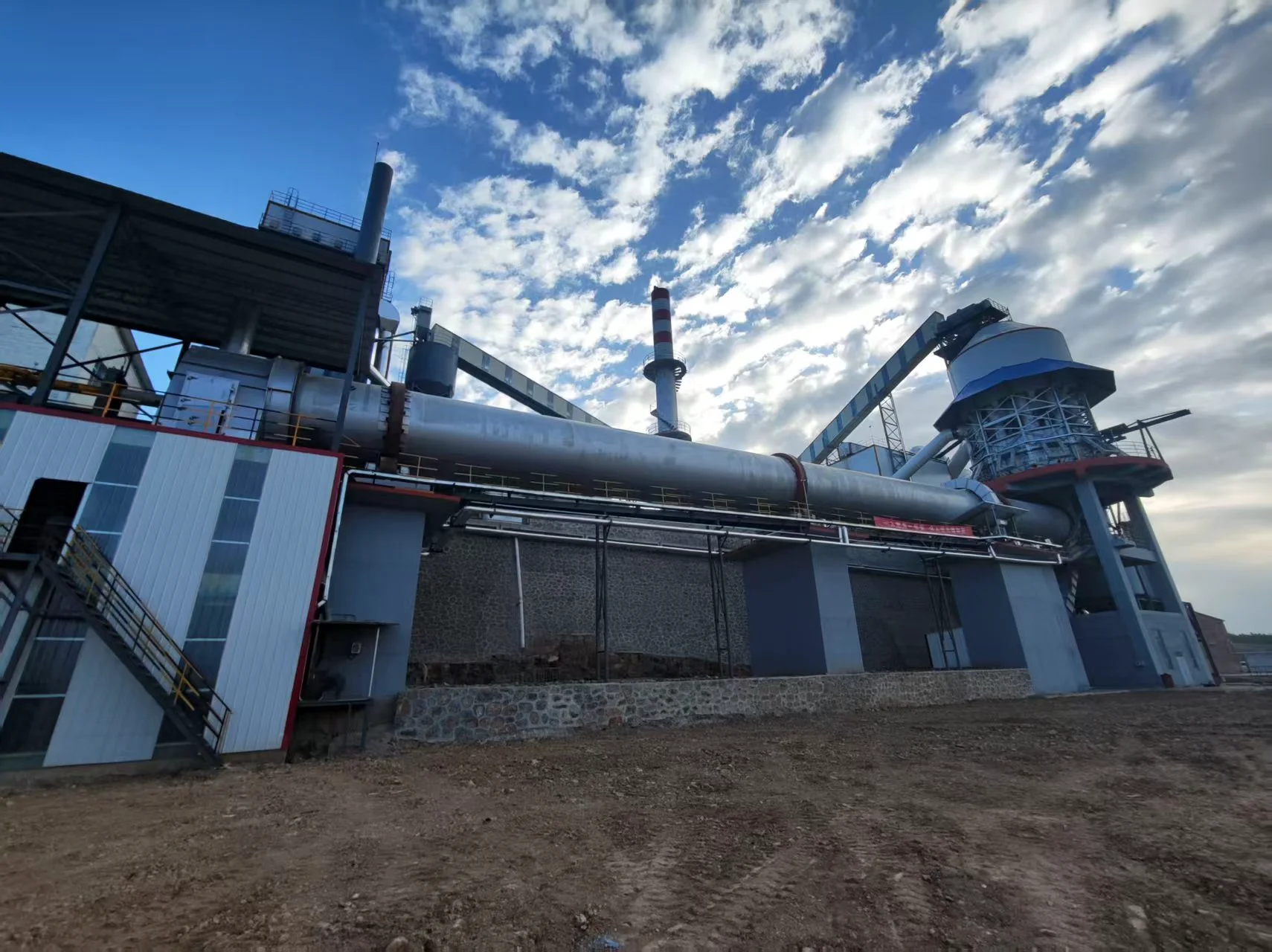
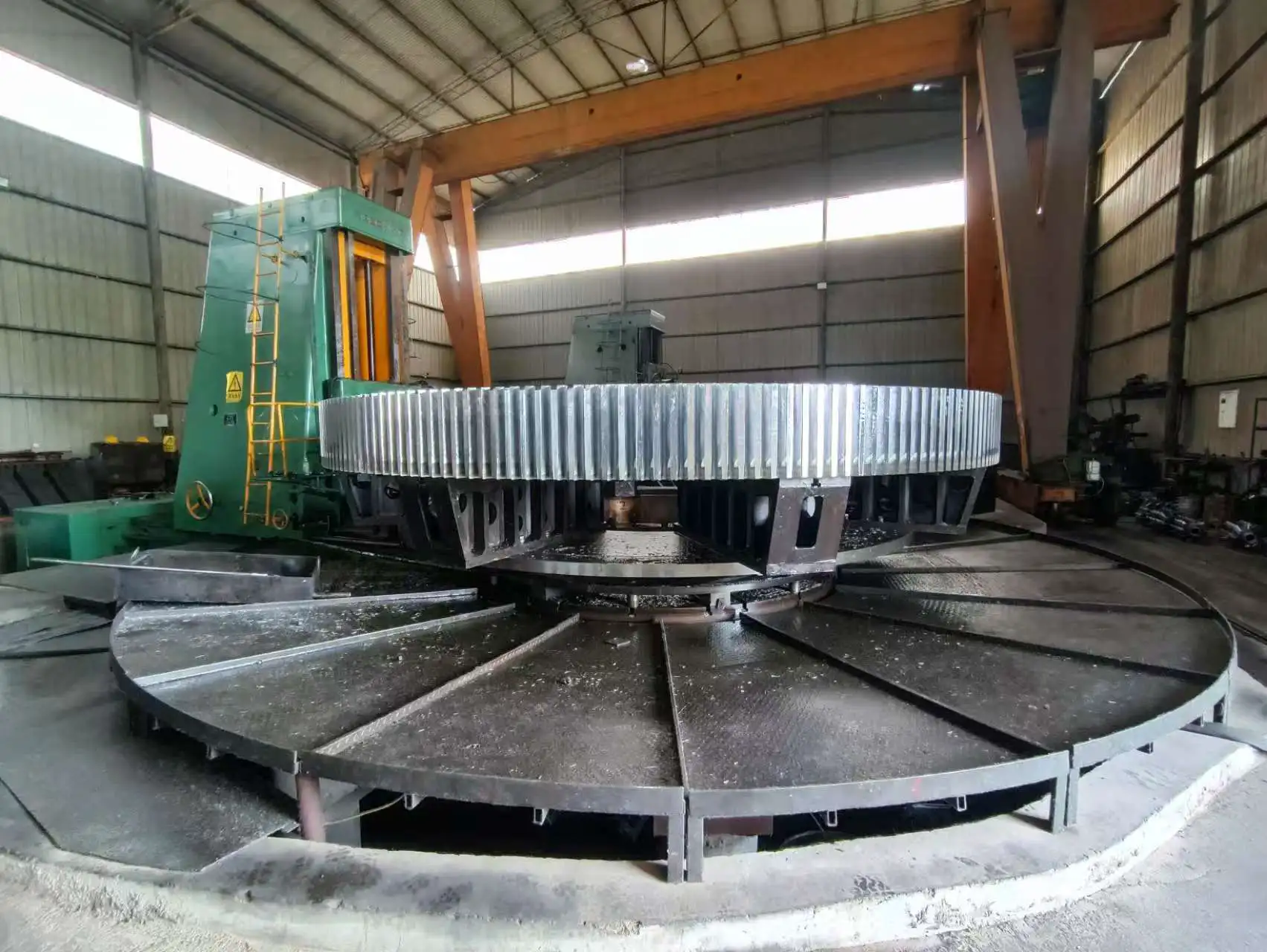
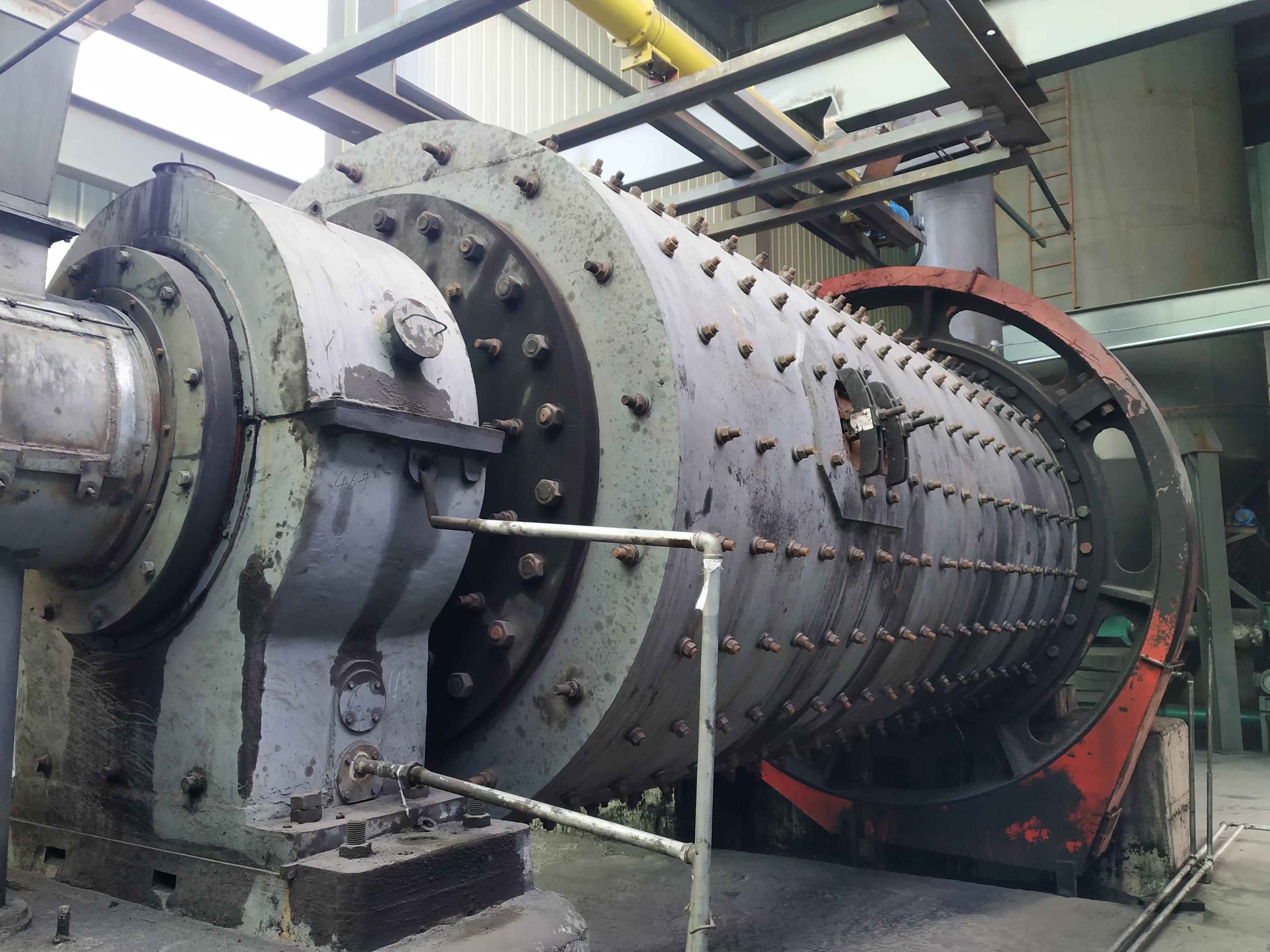
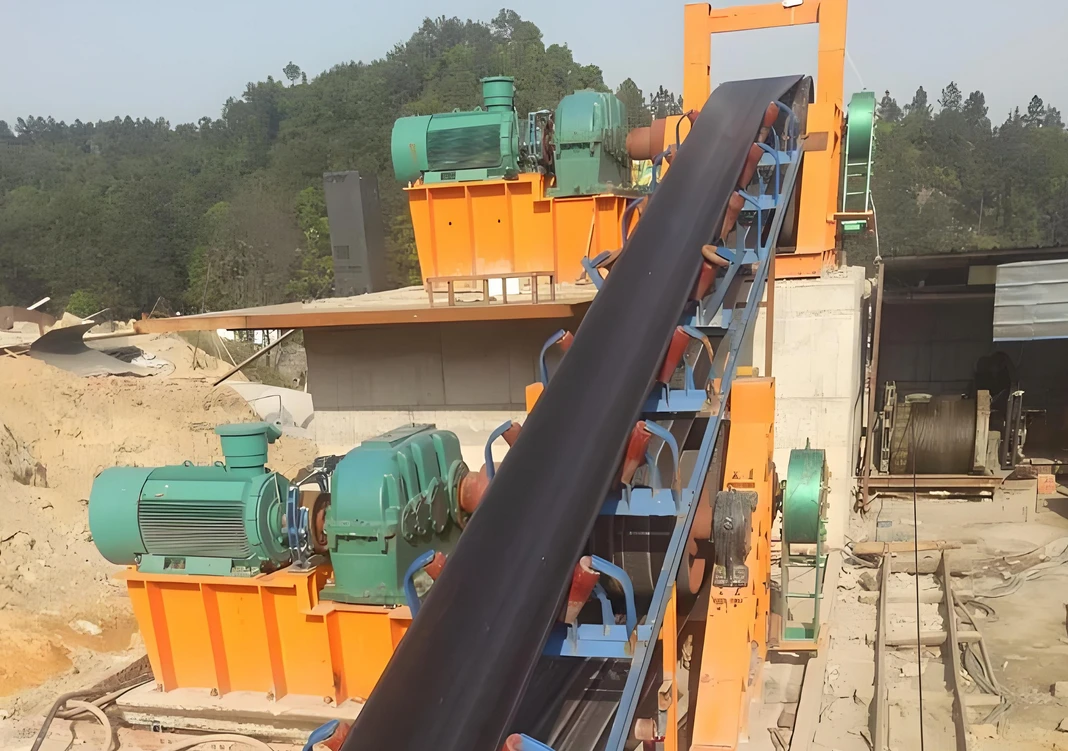
Customer site:




























